Welding vs. Bolted Pipe Clamps: Which Is Better for Your Project?
Author:Mingde Time:2025-12-17 18:24:20 Click:79
Expert Insights from a Pipe Clamp Manufacturer
Every piping system—whether part of an industrial plant, commercial facility, or utility network—depends on secure and reliable pipe support components. For a Pipe Clamp Manufacturer, one of the most common questions from project planners is whether welded or bolted pipe clamps offer better long-term performance. Each joining method comes with unique mechanical behaviors, installation demands, and structural benefits.
Understanding the differences between these two clamp styles can help engineers and buyers select a solution that enhances system integrity and minimizes future maintenance.


1. Why Joining Method Matters in Pipe Clamp Selection
Pipe clamps do far more than simply hold pipes in place. They stabilize the line, mitigate vibration, distribute weight, and prevent mechanical stress from damaging equipment. Because piping systems vary widely in temperature, load, and movement, the choice between welding and bolting directly influences the clamp’s service life and overall project efficiency.
Selecting the right method ensures the clamp works in harmony with the operating environment—not against it.
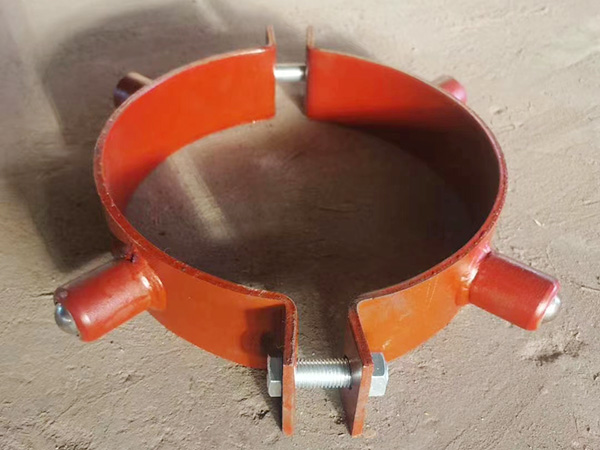
2. Welded Pipe Clamps: Built for Stability and Long-Term Strength
2.1 Benefits of a Welded Connection
Welded clamps are typically chosen for applications demanding maximum rigidity. Because the clamp is permanently fused to the mounting surface, welded solutions excel in environments with intense thermal cycling, high pressure, or dynamic stress. Advantages include:
·Exceptional structural stability
·Minimal movement under vibration
·Strong resistance to shifting or loosening
·Long-lasting reinforcement without routine adjustments
This makes welded clamps especially valuable in sectors where continuous industrial Production requires uninterrupted piping performance.
2.2 Situations Where Welding May Not Be Ideal
While welded clamps provide superior rigidity, there are limitations to consider:
·Installation requires certified welding professionals
·Heat exposure may affect nearby components
·Once installed, repositioning is difficult
·Repairs and inspection often require additional labor
Projects that anticipate frequent redesign or future rework may not benefit from the fixed nature of welded clamps.
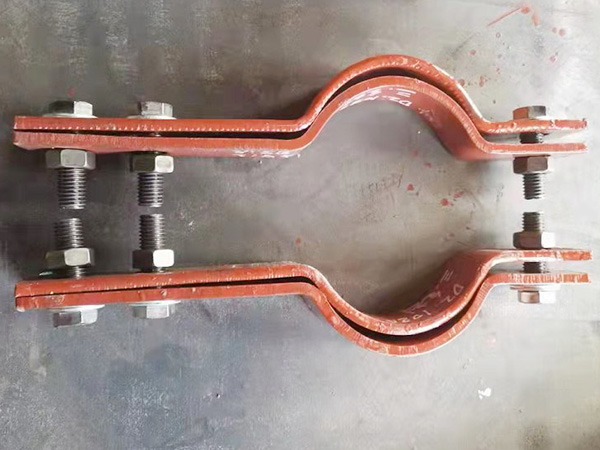
3. Bolted Pipe Clamps: Flexible, Accessible, and Easy to Maintain
3.1 Advantages of Bolted Designs
Bolted pipe clamps rely on mechanical fasteners rather than fusion, allowing for significantly greater flexibility. They are ideal for environments where installation speed and accessibility matter. Key advantages include:
·Quick assembly and disassembly
·No need for welding tools or heat-based processes
·Easy adjustment during system expansion
·Lower installation labor costs
·Preferred for routine maintenance or modular setups
These qualities make bolted clamps an efficient solution for commercial systems, utility lines, and facilities undergoing regular upgrades.
3.2 Where Bolted Clamps May Fall Short
Although bolted connections are convenient, they may require periodic attention:
·Bolts can loosen under high vibration
·Slightly lower rigidity than welded solutions
·May not withstand extreme temperature cycles as well
·Requires consistent torque checks in heavy-duty applications
For pipelines carrying high-pressure or high-temperature media, additional reinforcement mechanisms may be needed.


4. Technical Comparison: Welded vs. Bolted Pipe Clamps
4.1 Installation Requirements
Welding is more labor-intensive and demands strict safety procedures. Bolted clamps, however, can be installed by general technicians without specialized certification.
4.2 Durability and Load Resistance
Welded clamps generally provide superior weight-bearing capacity due to their fixed bonding. Bolted clamps offer good strength but may require washers, locking systems, or reinforced designs for high-load conditions.
4.3 Flexibility and System Modifications
If your project calls for future pipeline rerouting, expansions, or periodic inspection, bolted clamps clearly provide more convenience.
4.4 Long-Term Operational Demands
Welded clamps perform better in harsh environments with intense vibration, while bolted clamps excel in environments prioritizing accessibility.
5. Material Considerations and Environmental Factors
A knowledgeable Pipe Clamp Manufacturer evaluates material compatibility before recommending any clamp style. For instance:
·Stainless steel clamps are ideal for corrosion-prone environments
·Coated or galvanized clamps perform well in general-purpose industrial settings
·Carbon steel clamps provide robust support for heavy structures
Additionally, environmental exposure—such as humidity, temperature variance, or chemicals—affects the choice of joining method.
Welded clamps may require additional finishing for corrosion defense, while bolted designs often use corrosion-resistant hardware from the start.
6. Cost Perspectives: Installation vs. Lifecycle Economics
When comparing cost, welded solutions typically involve higher upfront labor expenses due to specialized welding processes. However, their long-term reliability can reduce total lifecycle costs in tough environments.
Bolted clamps offer fast and economical installation, making them an attractive option for large-scale Direct Supplier projects and budget-sensitive operations. They also allow easy replacement of components without dismantling the entire system.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Option with Guidance from a Pipe Clamp Manufacturer
Whether welding or bolting is the right choice depends on your system’s loads, temperatures, movement, and long-term accessibility requirements. A trusted Pipe Clamp Manufacturer can analyze your project needs, evaluate environmental conditions, and recommend a solution that balances safety, efficiency, and cost. Both methods have their place, and selecting the correct one ensures stable performance throughout the pipeline’s operational lifespan.
By understanding the trade-offs and benefits of each joining method, project planners can build stronger, more reliable piping systems that support smooth operations for years to come.
References
GB/T 7714:Erik Oberg F D J, Horton H L, Ryffel H H. Machinery’s Handbook[M]. Industrial Press, Inc., 2020.
MLA:Erik Oberg, Franklin D. Jones, Holbrook L. Horton, and HenryH Ryffel. Machinery’s Handbook. Industrial Press, Inc., 2020.
APA:Erik Oberg, F. D. J., Horton, H. L., & Ryffel, H. (2020). Machinery’s Handbook. Industrial Press, Inc..
 Hot Products
Hot Products
 Contact Us
Contact Us
Contact:
Mobile:+86 +86 19133378808
Website:mingdepipe.com
Address: