Selection of Connection Methods Between Pipe Supports and Piping Systems
Author:Mingde Time:2025-04-29 01:11:01 Click:120
The connection between pipe supports (or hangers) and pipelines is a critical design aspect in ensuring stability, load distribution, and system integrity. Choosing the appropriate connection method depends on factors such as pipe size, material, load type, movement allowances, and installation environment.
Below is a comprehensive guide to selecting the right connection method between pipe supports and piping systems.
1. Common Connection Methods
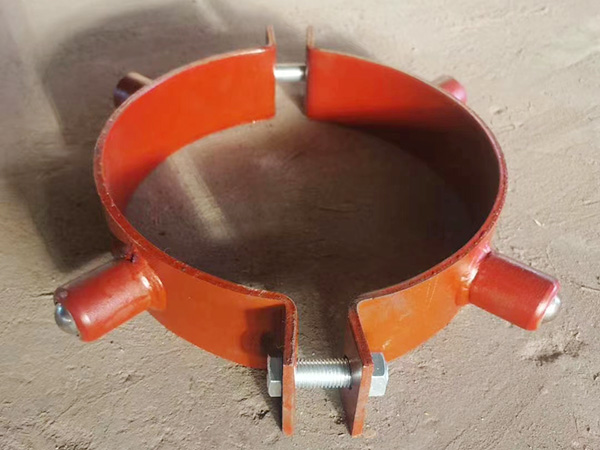
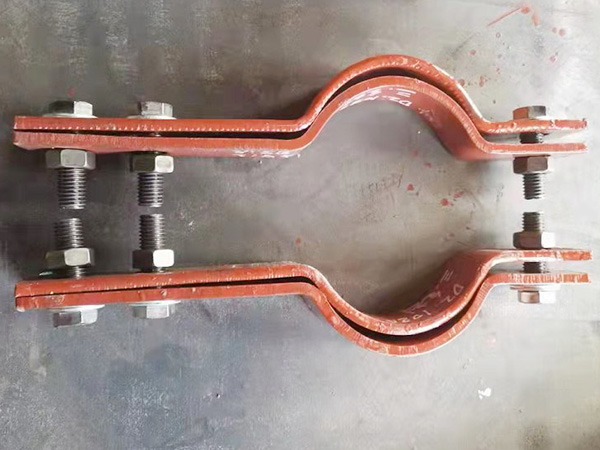
a. U-Bolts and Clamp-Type Connections
Description: U-bolts or clamps are directly fastened around the pipe to secure it to the support base or beam.
Advantages:
Simple and cost-effective
Easy to install and adjust
Best Used For:
Small to medium-diameter pipes
Rigid support points with minimal movement
Non-insulated or lightly insulated pipes
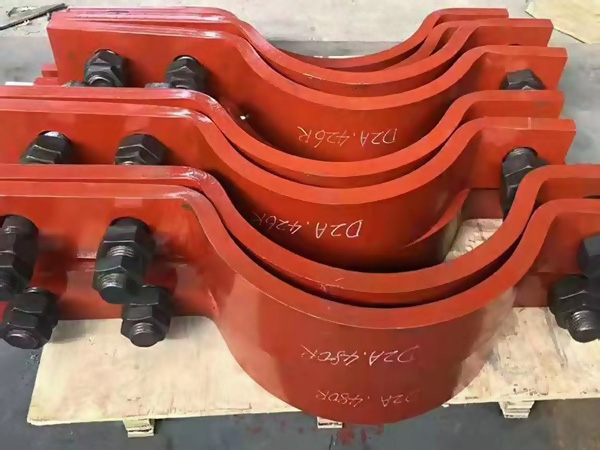
b. Pipe Saddles
Description: A curved support that conforms to the shape of the pipe, usually welded or bolted to the base support.
Advantages:
Distributes load evenly
Reduces stress on the pipe wall
Best Used For:
Large-diameter pipes
Heavily insulated or high-load applications
c. Hanger Rods and Clevis Hangers
Description: Pipes are suspended from structural elements using threaded rods and clevis-style hangers.
Advantages:
Accommodates vertical movement
Reduces vibration and dynamic stress
Best Used For:
Overhead piping in long runs
Systems requiring thermal movement control
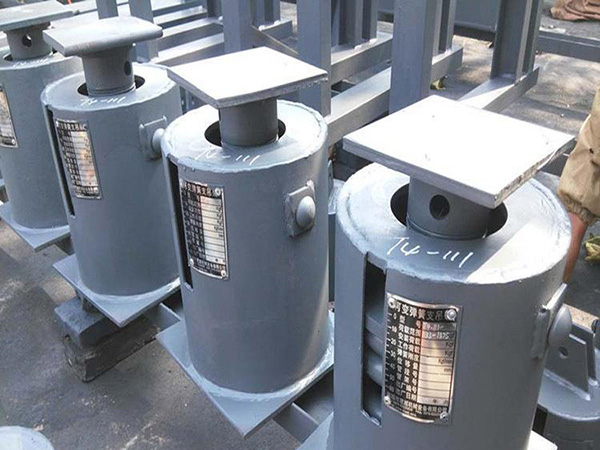
d. Spring Supports (Variable or Constant)
Description: Connected to the pipe via lugs, clamps, or pipe shoes, these supports allow vertical movement under load.
Advantages:
Balances pipe weight with movement
Ideal for high-temperature lines
Best Used For:
Steam or hot fluid lines
Equipment-connected pipes
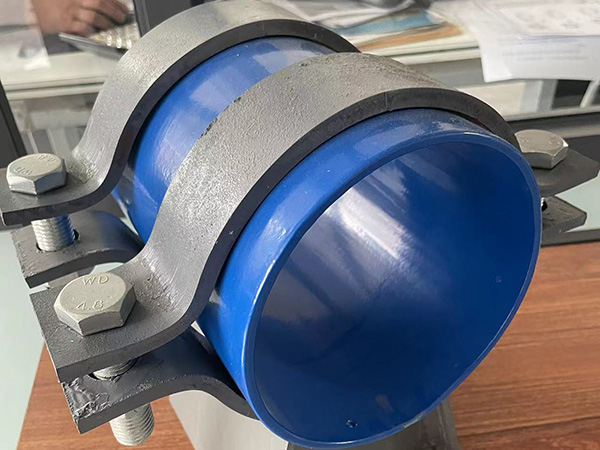
e. Pipe Shoes and Sliding Supports
Description: Shoes are welded or clamped to the pipe and rest on support beams with low-friction interfaces.
Advantages:
Allow axial thermal expansion
Prevent insulation damage and metal-to-metal contact
Best Used For:
Horizontal runs with thermal growth
Corrosive or high-temperature environments
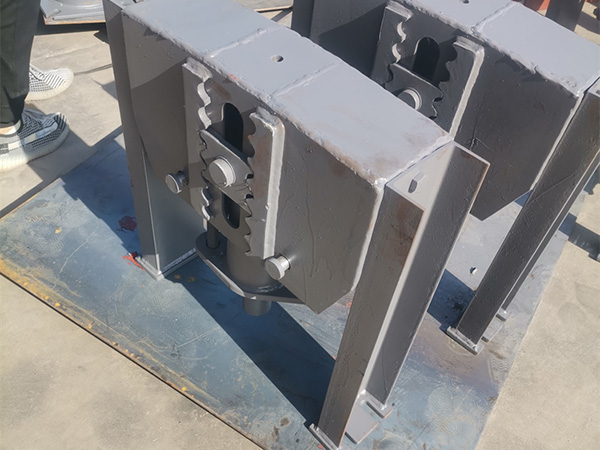
f. Welded Lugs and Brackets
Description: Steel lugs or brackets are directly welded to the pipe for rigid attachment.
Advantages:
High load-bearing capacity
Permanent and secure
Best Used For:
Anchors and fixed points
Systems with zero relative movement
2. Key Factors in Connection Method Selection
a. Pipe Material and Wall Thickness
Thin-walled or non-metallic pipes may require non-intrusive or cushioned supports.
Avoid welded connections for pipes with special coatings or liners.
b. Operating Temperature and Expansion
For high-temperature systems, use sliding or spring-type connections to accommodate movement.
Rigid connections are suitable for ambient temperature lines.
c. Load Type and Direction
Vertical loads → Clevis hangers, spring hangers
Horizontal thermal expansion → Sliding supports, guided shoes
Lateral loads → Bracketed or anchored supports
d. Installation Environment
Outdoor or corrosive environments → Use corrosion-resistant hardware (e.g., galvanized or stainless steel)
Clean rooms or food-grade facilities → Hygienic clamp systems with minimal crevices
3. Recommendations for Optimal Design
Combine connection types: Mix rigid and flexible supports to balance stability and movement.
Allow movement where needed: Avoid over-restraining pipes which can lead to fatigue or failure.
Ensure proper alignment: Misaligned connections increase stress and reduce system lifespan.
Regular inspection: Verify tightness, corrosion, and alignment in long-term operation.
Conclusion
The choice of pipe-to-support connection method significantly impacts the performance, durability, and safety of a piping system. By carefully evaluating pipe characteristics, load demands, and environmental factors, engineers can design efficient support systems that ensure long-term reliability with minimal maintenance.
 Hot Products
Hot Products
 Contact Us
Contact Us
Contact:
Mobile:+86 +86 19133378808
Website:mingdepipe.com
Address: