Cryogenic Pipeline Support Standards
Author:Mingde Time:2025-11-28 17:52:45 Click:62
Why Pipe Support Systems Matter in Cryogenic Transport
Cryogenic pipelines operate in a temperature regime where traditional industrial materials quickly lose toughness, expand or contract excessively, and become vulnerable to structural instability. In these extreme settings, Pipe Support Systems must deliver far more than simple load-bearing—they must protect insulation, accommodate thermal movement, and minimize heat transfer.
Because of the complexity of these projects, engineering firms often depend on a Manufacturer with established Production capability to supply standardized, precision-engineered supports. Reliable large-batch output ensures consistent quality across entire pipeline systems, which is critical in cryogenic service.
This article outlines the engineering standards and design principles that govern safe, long-term performance of cryogenic pipeline supports.


How Cryogenic Conditions Transform Piping Requirements
Pipelines transporting liquefied gases—such as LNG, LOX, LH₂, or liquid ammonia—are continuously exposed to temperatures from below −50°C down to −196°C. At these temperatures:
·Metals contract significantly
·Mechanical properties change dramatically
·Insulation becomes critical for safety
·Support spacing and load calculations shift
·Normal steelwork risks freezing or moisture penetration
These factors make cryogenic support design a specialized discipline requiring strict adherence to established standards.
Primary Engineering Standards for Cryogenic Pipe Support Systems
1. ASME B31.3 – The Baseline Code for Process Piping
ASME B31.3 is one of the most referenced codes for process piping around the world. Its cryogenic guidelines emphasize:
·Correct low-temperature allowable stresses
·Thermal displacement analysis
·Controlled flexibility for contraction
·Protection against over-constrained support layouts
For cryogenic applications, designers often incorporate cold shoes, sliding plates, and optimized anchor points to comply with B31.3 requirements.
2. API Equipment Loading Rules (API 610 / API 617)
Though focused on rotating machinery, these API standards still influence cryogenic pipeline support strategy. They provide limits for:
·Acceptable piping loads at equipment nozzles
·Vibration control expectations
·Thermal contraction effects near pumps or compressors
Proper support placement minimizes the transfer of unwanted forces to connected equipment.
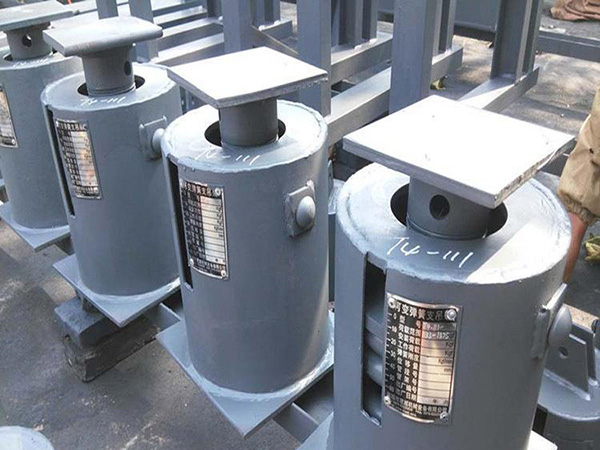
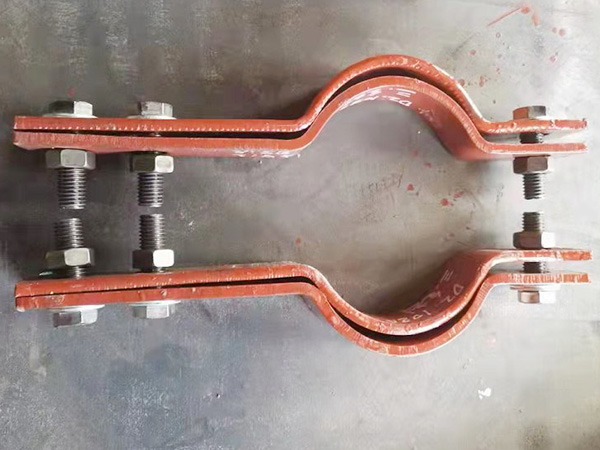
3. MSS SP-58, SP-69, and SP-89 – Defining Pipe Support Geometry and Performance
The MSS standards form the backbone of support fabrication rules. They define:
·Types of hangers, guides, clamps, and shoes
·Support dimensions and mechanical capacity
·Materials that maintain toughness at cryogenic temperatures
·Inspection and installation requirements
Cryogenic support assemblies often combine MSS geometries with high-density insulation blocks to prevent heat flow into the pipeline.
4. ASTM Material Standards for Cryogenic Durability
ASTM specifications govern the performance of steels and insulation materials used in cryogenic service. Common examples include:
·ASTM A240 stainless steel for low-temperature support shoes
·ASTM A350 LF2/LF3 for structural components
·ASTM C552, C534, C591 for load-bearing insulation
These materials withstand thermal shock, maintain structural strength, and resist moisture absorption.
5. EN 13480 – European Rules for Industrial Metallic Piping
EN 13480 provides an international standard framework where:
·Cryogenic loads and movements are defined mathematically
·Support categories (fixed, guide, sliding) are standardized
·Fabrication quality and corrosion resistance are specified
·Inspection procedures ensure life-cycle performance
Many global engineering firms adopt EN 13480 for LNG and hydrogen projects.
Key Design Principles for Cryogenic Pipe Support Systems
1. Managing Thermal Contraction
Cryogenic pipelines shrink considerably, so supports must allow controlled movement. Engineers typically integrate:
·Sliding plates with PTFE or stainless steel
·Flexible supports positioned at calculated intervals
·Anchors placed only where necessary
Improper restraint can lead to severe pipe stress or misalignment.
2. Preserving Insulation Continuity
The insulation layer around a cryogenic pipe is essential for preventing:
·Energy loss
·Frost accumulation
·Moisture ingress
·Structural freezing
Support systems therefore use rigid, load-bearing insulation bodies that maintain shape and strength even under heavy compression.
3. Ensuring Proper Load Distribution
Cryogenic pipelines, especially with thick insulation, are heavier than standard process lines. Engineers must consider:
·Total supported weight
·Thermal expansion forces
·Seismic loading depending on region
·Vibration from connected equipment
Accurate load calculations prevent sagging, displacement, and overstress.
4. Controlling Heat Flow and Avoiding Cold Bridges
One of the biggest design risks is unintended thermal bridging. Cryogenic supports must:
·Minimize heat transfer
·Incorporate low-conductivity material layers
·Avoid exposing pipe metal directly to structural steel
These measures protect both the pipeline and nearby structures.
Why Manufacturer-Level Production Quality Matters
Cryogenic pipe supports are not generic hardware—they are engineered components requiring advanced material selection, tight fabrication tolerances, and precise insulation machining.
A Manufacturer with proven Production capacity offers several advantages:
·Uniformity across hundreds or thousands of supports
·Reliable machining tolerances to prevent misalignment
·Verified compliance with ASME, MSS, ASTM, and EN codes
·Strong QC processes that prevent material defects
In large-scale LNG, hydrogen, and air separation facilities, consistent manufacturing quality is essential for safe long-term operation.
Conclusion: Standards Ensure Safe and Reliable Cryogenic Pipeline Support
Cryogenic pipelines impose engineering challenges that exceed those found in normal industrial systems. By following international standards and selecting properly engineered Pipe Support Systems, engineers ensure:
·Safe thermal contraction management
·Durable insulation protection
·Accurate load transfer
·Compliance with ASME, MSS, API, ASTM, and EN guidelines
Choosing a Manufacturer capable of stable, high-volume Production is key to maintaining uniform quality and reliability across the entire pipeline.
High-performance cryogenic pipe supports are not optional—they are foundational to the integrity, efficiency, and safety of every cryogenic pipeline installation.
References
GB/T 7714:SP A. 69-Pipe Hangers and Supports-Selection and Application; Manufacturers Standardization Society of the Valve and Fittings Industry[J]. 2003.
MLA:SP, ABMSS. "69-Pipe Hangers and Supports-Selection and Application; Manufacturers Standardization Society of the Valve and Fittings Industry." (2003).
APA:SP, A. (2003). 69-Pipe Hangers and Supports-Selection and Application; Manufacturers Standardization Society of the Valve and Fittings Industry.
 Hot Products
Hot Products
 Contact Us
Contact Us
Contact:
Mobile:+86 +86 19133378808
Website:mingdepipe.com
Address: