Guide to Pipeline Insulation Supports: Key Features, Applications, and Selection Strategies
Author:Mingde Time:2025-06-14 15:29:45 Click:198
I. Introduction
(A) Engineering Background of Pipeline Insulation Supports
In the operation of industrial pipeline systems, pipeline insulation supports serve as a core component of the thermal management system, playing a crucial role in energy efficiency, system stability, and equipment lifespan. With the deepening of global energy conservation and environmental protection concepts and stricter policy requirements, the importance of their technological application has become increasingly prominent.
(B) Core Functions of Insulation Supports
Pipeline insulation supports significantly reduce heat loss and prevent condensation by effectively controlling heat conduction, stabilizing pipeline loads, and avoiding the occurrence of cold bridges. This not only ensures the safe and efficient operation of pipeline systems but also optimizes economic costs.
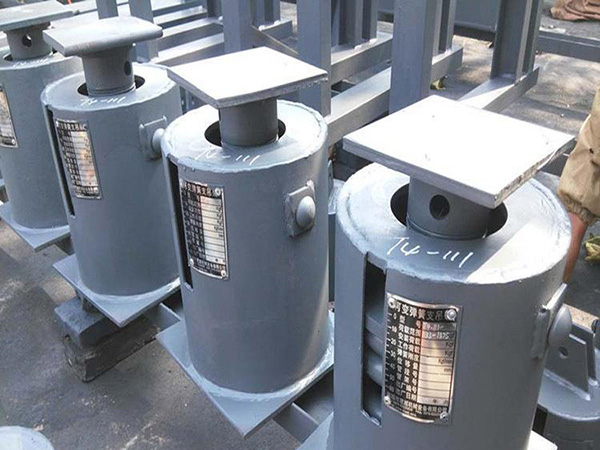
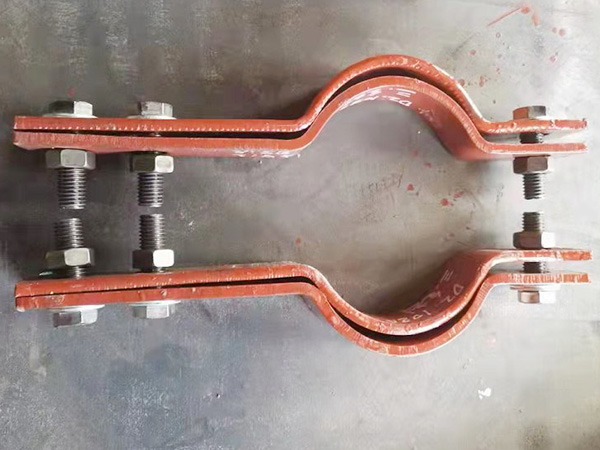
II. Key Features of Pipeline Insulation Supports
(A) Material Characteristics
Insulation Material Types
Polymer composites effectively block heat transfer due to their low thermal conductivity.
Ceramic fiber and glass fiber exhibit excellent high-temperature insulation properties, suitable for high-temperature environments.
Polyurethane foam offers both insulation and waterproofing functions in low-temperature environments.
Support Structure Materials
Stainless steel ensures stability and durability with its excellent corrosion resistance and high strength.
Aluminum alloy is lightweight and has good weather resistance, facilitating installation and adapting to various environments.
Engineering plastics possess insulation and chemical stability, suitable for special media environments.
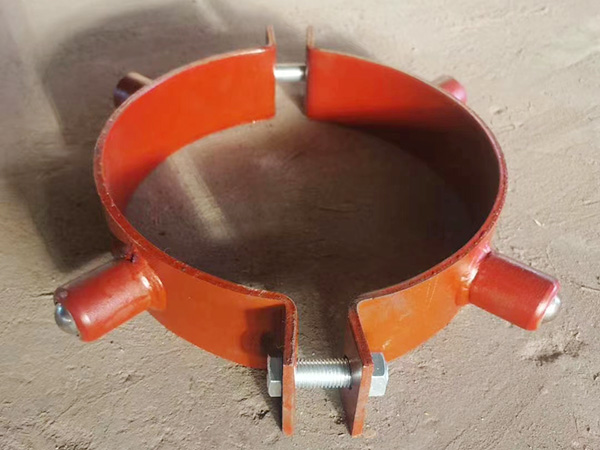
(B) Structural Design Features
Composite Structure of Insulation and Support Layers
Double-layer insulation design enhances insulation effects by blocking heat conduction paths.
Elastic support structures effectively buffer vibrations, reducing pipeline wear caused by vibrations.
Installation Adaptability Design
Adjustable supports can flexibly accommodate pipes of different diameters, improving versatility.
Modular structural design facilitates on-site installation and later stage maintenance, enhancing construction efficiency.
(C) Performance Indicators
Thermal Conductivity (λ Value): A key indicator for measuring the insulation performance of supports.
Load-Bearing Capacity: Determines the weight and pressure range that supports can withstand.
Temperature Resistance Range: Covers adaptability in both high-temperature and low-temperature environments.
Anti-Aging and Weather Resistance: Reflects the stability and durability of supports during long-term use.
III. Application Scenarios of Pipeline Insulation Supports
(A) Industrial Pipeline Sector
Petrochemical Industry
Used for high-temperature steam pipelines to reduce heat loss and improve energy efficiency.
Ensures the normal operation of low-temperature liquefied gas pipelines, preventing condensation.
Energy and Power Industry
Provides reliable insulation and support for steam pipelines in thermal power plants.
Meets the stringent requirements for insulation and fixation of cooling pipelines in nuclear power plants.
(B) Construction and Municipal Engineering
Central Heating Systems
Offers an integrated solution for insulation and support of heating pipelines, ensuring efficient heat transmission.
Chilled Water Pipelines
Prevents condensation problems in refrigerant pipelines of air conditioning systems, maintaining system stability.
(C) Special Environmental Applications
Marine Engineering
Resists high salt spray environments on offshore platforms, providing corrosion-resistant pipeline insulation support.
Polar Engineering
Solves thermal management challenges for pipelines in low-temperature environments, ensuring normal system operation.
IV. Selection Strategies for Pipeline Insulation Supports
(A) Environmental Parameter Analysis
Temperature Condition Assessment
Select materials with high heat resistance for high-temperature conditions.
Focus on the freeze-cracking resistance of materials for low-temperature conditions.
Medium Characteristic Considerations
Choose materials with corresponding corrosion resistance levels for corrosive media.
Prioritize fire safety performance of materials for flammable and explosive media.
(B) Engineering Technical Requirements
Pipeline Parameter Matching
Precisely select support specifications according to pipe diameter and wall thickness.
Consider pipeline thermal expansion and reasonably design compensation schemes.
Installation Space Constraints
Choose compact supports for narrow spaces to save installation space.
Adopt lightweight designs for high-altitude operations to reduce construction difficulty.
(C) Cost and Standard Compliance
Full Life Cycle Cost Assessment
Balance initial procurement costs with long-term maintenance costs.
Analyze the impact of energy-saving benefits on overall investment returns.
Industry Standard Compliance
Ensure compliance with domestic standards (such as GB/T 28638).
Meet international standards (such as ASME, EN) to adapt to different project requirements.
V. Installation and Maintenance Guidelines
(A) Installation Technical Specifications
Follow positioning and spacing design principles to ensure a reasonable support layout.
Adopt effective methods to ensure the continuity of insulation layers and prevent heat leakage.
Strictly implement waterproof sealing processes to prevent moisture intrusion and performance degradation.
(B) Maintenance and Inspection Strategies
Establish a periodic thermal performance testing mechanism to promptly detect performance degradation issues.
Master the identification points for aging and damage to quickly locate faults.
Develop emergency repair and replacement plans to ensure rapid restoration of pipeline systems in case of failures.
VI. Conclusion and Trend Outlook
(A) Summary of Key Selection Points
The selection of pipeline insulation supports requires comprehensive consideration of material characteristics, environmental conditions, engineering requirements, costs, and standards to achieve the best fit.
(B) Technological Development Trends
Smart monitoring insulation supports will enable real-time performance monitoring and early warning through integrated sensors.
The development and application of degradable and environmentally friendly materials will drive the industry towards green and sustainable development.
 Hot Products
Hot Products
 Contact Us
Contact Us
Contact:
Mobile:+86 +86 19133378808
Website:mingdepipe.com
Address: