High-Quality Insulated Pipe Supports: A Key Element for System Stability
Author:Mingde Time:2025-07-14 17:30:57 Click:165
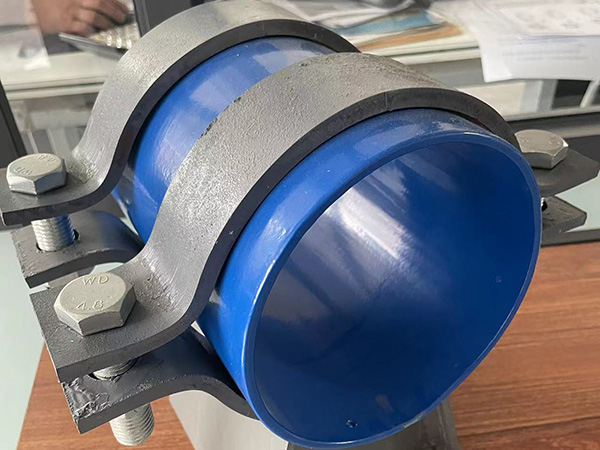
In industrial piping systems, insulated pipe supports not only bear the structural load of pipelines but also play a crucial role in thermal insulation, vibration control, and overall system stability. Especially in applications such as high-temperature steam, district heating, and heat recovery, well-designed and properly selected pipe supports are essential for improving operational efficiency and extending service life. This article explores the core technical elements of modern insulated pipe supports, focusing on materials, structural design, and installation methods.
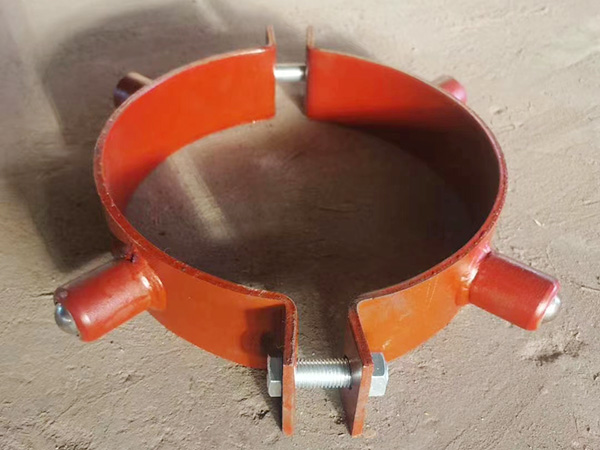
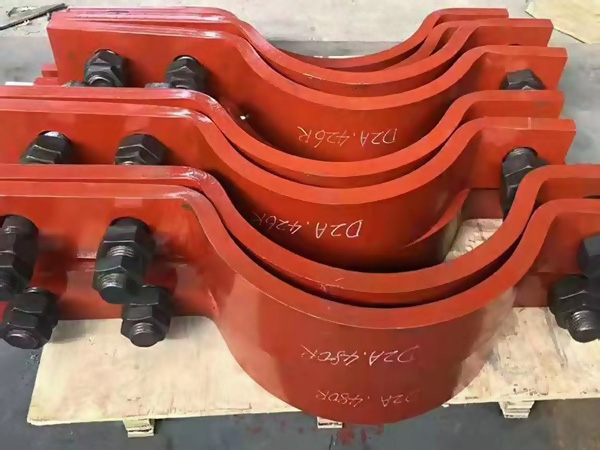


I. Material Applications: Balancing Thermal Performance and Environmental Durability
1. Multi-Layer Composite Structures for Enhanced Insulation
High-performance insulated pipe supports often adopt composite thermal insulation layers based on high-density polyurethane, combined with materials like rock wool or ceramic fiber. While thermal conductivity as low as 0.022 W/(m·K) is achievable in ideal lab conditions, real-world performance depends on robust structural integrity and tight integration with support frames. Therefore, selecting a support system with well-engineered insulation and mechanical stability—rather than just low-conductivity materials—is critical for long-term energy efficiency.
2. Weather and Corrosion Resistance
In high-humidity, salt-laden, or chemically aggressive environments, the outer shell of the support is typically made from stainless steel or galvanized steel, coated with high-temperature protective finishes. These coatings offer UV resistance and chemical durability. In extreme climates, infrared-reflective coatings are sometimes added to reduce surface heat absorption and extend service life.

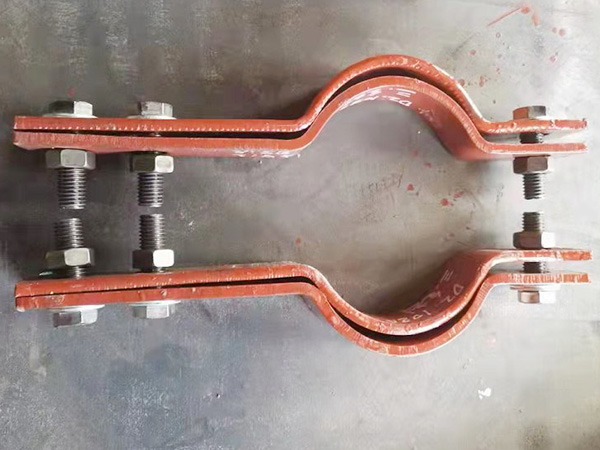
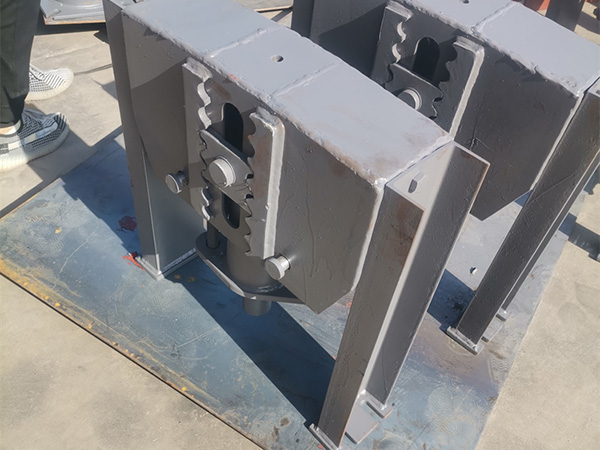
II. Structural Design: Balancing Load Bearing and Thermal Expansion
1. Coordinated Use of Fixed and Sliding Supports
Modern engineering emphasizes dynamic balance in support systems between load-bearing and thermal expansion. Fixed supports restrict axial movement, while sliding or spring-type supports accommodate expansion and contraction. Proper layout and stress simulation help reduce the risk of stress concentration and deformation due to thermal movement.
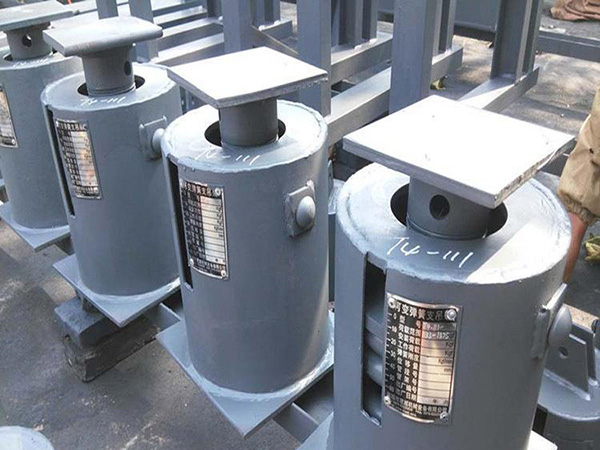
2. Enhanced Stability and Vibration Control
For thin-walled or large-diameter pipes, structural instability is a key concern. Features such as reinforcement ribs and compression rings can improve local resistance to deformation. Additionally, rubber or composite damping pads at the support base help mitigate vibrations caused by seismic activity or fluid pulsation, thereby improving system safety.
III. Installation Techniques: Standardization and Smart Integration for Quality Assurance
1. Modular Quick-Assembly Systems
Insulated pipe supports are increasingly designed for modularity and prefabrication. Fastening methods such as clips, flanges, or bolts enable efficient on-site installation. Components are pre-sized and designed to prevent water ingress, reducing the need for welding or secondary adjustments—making them ideal for district heating and industrial systems.
2. Condition Monitoring and Remote Diagnostics
With the advancement of digital technology, some next-generation insulated pipe supports are being designed to integrate sensors for condition monitoring. However, widespread industrial adoption still hinges on reliable mechanical design, robust insulation, and field-proven durability. Therefore, for most applications, mechanical reliability and ease of maintenance remain the core evaluation criteria, with smart features acting as value-added options.
IV. Technology Trends: Lightweighting, Integration, and Standardization
Industry development is moving toward the adoption of high-strength lightweight materials, standardized interfaces, and integrated functions. Industry innovation is gradually exploring areas such as high-performance composites, modular structural optimization, and adaptive design principles. However, real-world adoption continues to rely on mature, standardized insulated pipe supports that combine proven materials and structural reliability. For manufacturers and end users alike, balancing innovation with long-term maintainability remains key to success.These trends provide a competitive pathway for Pipe Clamp Manufacturers in the global market.
International References
Zenkert, D. (1997). The Handbook of Sandwich Construction. Engineering Materials Advisory Services Ltd.
Jain, A.,Kandlikar, S. G. (2007). Enhanced Heat Transfer Using Nanofluids in Industrial Applications, International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 50(15–16), 3076–3088.
Li, Y., et al. (2019). Development of Modular Pipe Supports with Improved Thermal Isolation for District Heating Networks, Applied Thermal Engineering, 149, 1241–1249.
 Hot Products
Hot Products
 Contact Us
Contact Us
Contact:
Mobile:+86 +86 19133378808
Website:mingdepipe.com
Address: