Industrial Insulation Bracket Design: High-Pressure and Extreme-Temp Standards
Author:Mingde Time:2025-09-11 01:37:39 Click:143
Pipe Support Systems as the Hidden Backbone
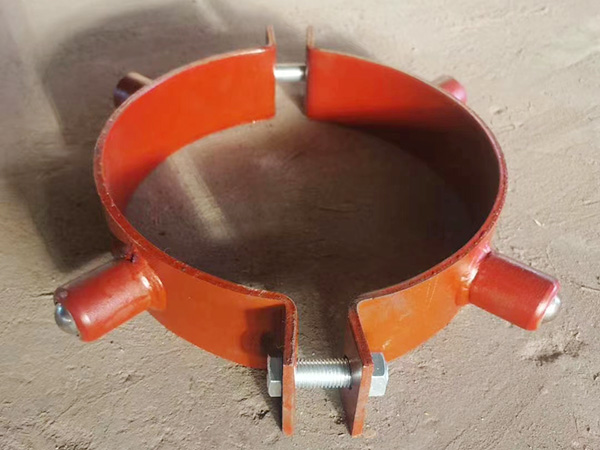
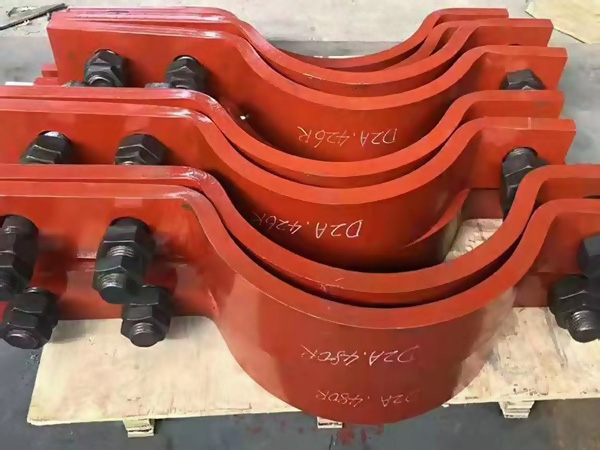
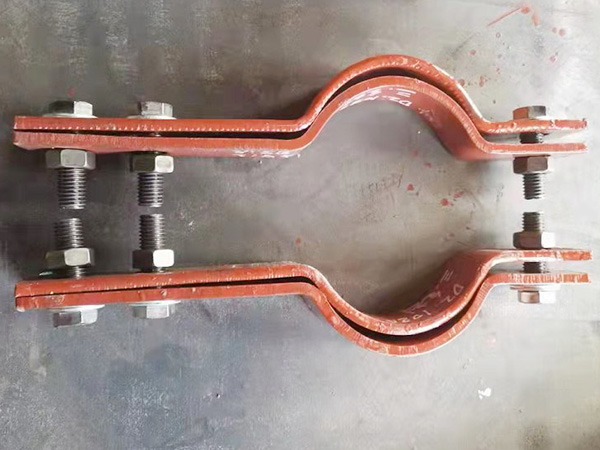
Every large-scale facility, from refineries to power plants, relies on pipe support systems to keep critical operations stable. Pipes that carry pressurized steam, cryogenic liquids, or corrosive chemicals require more than just insulation—they demand specialized brackets capable of maintaining structural integrity under the harshest conditions. These insulation brackets are not mere accessories; they are engineered solutions designed according to strict industrial standards to ensure reliability and safety.
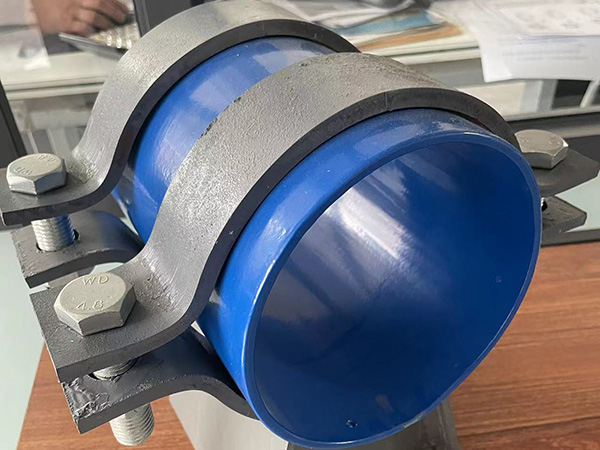
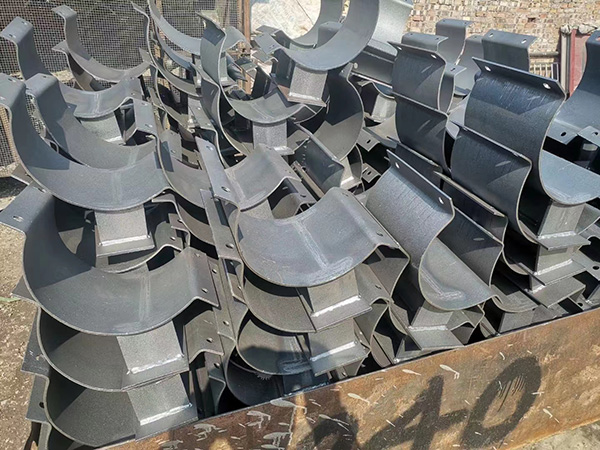


Why Strict Design Standards Are Essential
If pipe supports are built without standards, the risks are immediate and severe. Potential consequences include:
·Significant thermal losses from poorly insulated junctions
·Structural misalignment or sagging of pipelines
·Escalating maintenance costs due to premature wear
·Safety incidents triggered by system breakdowns
For these reasons, adherence to formal design protocols is non-negotiable. Standardized approaches guarantee that pipe support systems perform effectively across their entire service life.
Key Engineering Criteria for Insulation Brackets
1. Structural Strength
Insulation brackets must bear the combined forces of pipelines, insulation materials, and moving fluids. Engineering calculations account for vibration, pressure shifts, and expansion stresses.
2. Thermal Continuity
The bracket zone often becomes a thermal weak point. To minimize this effect, designers use advanced materials such as phenolic inserts, composites, or coated metals that preserve insulation performance.
3. Material Endurance
Brackets in corrosive or high-pressure conditions are typically manufactured from stainless steel or specialty alloys that resist fatigue, oxidation, and chemical damage.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Safety standards require brackets to function under abnormal conditions—whether during seismic activity, thermal surges, or fire exposure—without catastrophic failure.
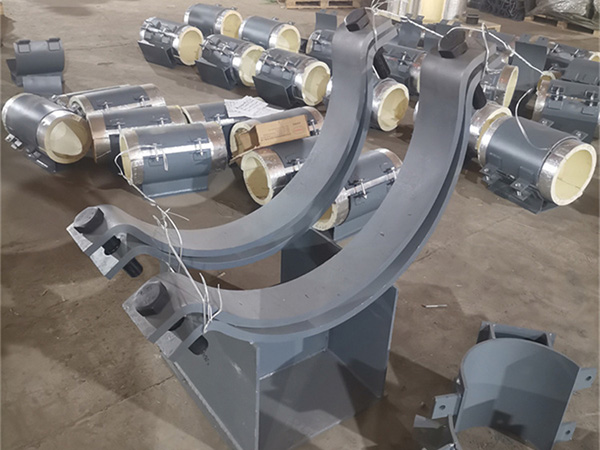
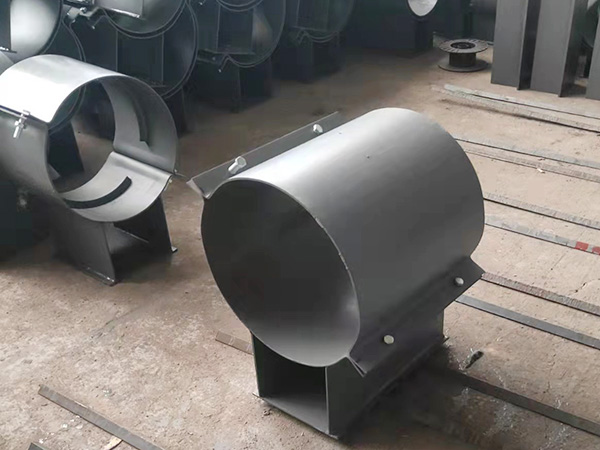


Environmental Factors in Design
Different facilities impose unique stresses on pipe support systems, demanding tailored design considerations:
·High-Pressure Pipelines: Supports must control forces generated by elevated internal pressure, distributing them evenly to prevent insulation collapse.
·Cryogenic Systems: At extremely low temperatures, materials can lose flexibility, so brackets must resist brittleness and thermal shock.
·High-Heat Operations: Facilities moving superheated fluids require supports that tolerate expansion cycles without compromising insulation.
·Corrosive Environments: Offshore or chemical plants rely on coated or alloy-based supports that maintain structural integrity over years of exposure.
Verification Through Testing
Robust design is only proven when validated under controlled testing conditions:
·Mechanical load tests simulate vibration and dynamic forces.
·Thermal efficiency tests measure the degree of heat transfer across the bracket.
·Corrosion simulations replicate decades of exposure in condensed timeframes.
·Safety compliance checks align systems with international codes and regional regulations.
These assessments confirm that insulation brackets are fit for long-term use in extreme operating environments.
Best Practices for Installation
Even the strongest design can fail if improperly installed. Recommended practices include:
·Ensuring alignment along the pipe axis to avoid uneven load distribution
·Preventing over-compression of insulation by careful tightening
·Using compatible fasteners to avoid galvanic corrosion
·Scheduling inspections to identify early wear or misalignment in high-stress environments
These measures ensure that pipe support systems deliver consistent performance over decades of operation.
Operational Advantages of Standards-Based Systems
When industries adopt brackets engineered to meet design standards, the benefits are measurable:
·Improved energy efficiency – Less heat loss translates into reduced operating costs.
·Extended equipment longevity – Supports protect pipes and insulation against premature failure.
·Lower unplanned downtime – Systems designed for resilience experience fewer breakdowns.
·Enhanced workplace safety – Personnel and assets are better shielded against catastrophic failures.
Ultimately, the use of compliant pipe support systems is an investment in stability, cost control, and worker safety.
Conclusion: Building Reliability with Pipe Support Systems
Insulation brackets for industrial-grade pipelines must be engineered with precision, tested against strict benchmarks, and installed with best practices. In applications where pressures soar, temperatures fluctuate, and environments corrode, compliance with design standards is what separates reliable performance from costly disruptions.
By selecting the right materials, prioritizing safety, and following established codes, industries can build pipe support systems that protect energy efficiency, extend infrastructure lifespan, and guarantee safety in even the harshest environments.
References
GB/T 7714:E&T P T P. STRESS ANALYSIS EVALUATION AND PIPE SUPPORT TYPE ON HIGH-PRESSURE AND TEMPERATURE STEAM PIPE[J]. 2023.
MLA:E&T, PT Pustek. "STRESS ANALYSIS EVALUATION AND PIPE SUPPORT TYPE ON HIGH-PRESSURE AND TEMPERATURE STEAM PIPE." (2023).
APA:E&T, P. P. (2023). STRESS ANALYSIS EVALUATION AND PIPE SUPPORT TYPE ON HIGH-PRESSURE AND TEMPERATURE STEAM PIPE.
 Hot Products
Hot Products
 Contact Us
Contact Us
Contact:
Mobile:+86 +86 19133378808
Website:mingdepipe.com
Address: