Solving Flange Distortion Challenges
Author:Mingde Time:2025-04-28 21:59:50 Click:54
Flange deformation is a critical issue leading to leaks, joint failures, and safety risks in piping systems. Below is a structured approach to diagnose causes, prevent distortion, and implement solutions.
1. Common Causes of Flange Distortion
A. Thermal Stress
Uneven Heating/Cooling: Differential expansion between flange/bolts.
Cyclic Thermal Fatigue: Repeated temperature swings causing warping.
B. Mechanical Loads
Over-Torquing Bolts: Excessive force bending flange faces.
Piping Misalignment: Angular forces during operation.
External Weight/Vibration: Unsupported pipe loads or machinery-induced stress.
C. Material & Manufacturing Defects
Casting/Forging Flaws: Micro-cracks or residual stresses.
Poor Machining: Out-of-flatness (>0.05mm deviation from ASME B16.5).
Incorrect Material Grade: Low-temperature embrittlement or creep at high temps.
2. Detection & Assessment
Visual Inspection: Gaps using feeler gauges or straightedges.
Laser Scanning: 3D mapping of flange face flatness.
Ultrasonic Testing (UT): Detects subsurface cracks.
Bolt Load Monitoring: Wireless sensors for real-time tension tracking.
3. Prevention Strategies
A. Design Phase
Flange Selection:
Use raised face (RF) or ring-type joint (RTJ) for high-pressure systems.
Upgrade to forged (not cast) flanges for critical services.
Finite Element Analysis (FEA): Simulate thermal/mechanical stresses.
B. Installation Best Practices
Controlled Bolt Tightening:
Follow ASME PCC-1 torque sequence (star pattern).
Use hydraulic tensioners for even load distribution.
Alignment Verification:
Laser alignment tools for pipe-flange concentricity.
Shim gaps >0.1mm before bolting.
C. Operational Mitigation
Thermal Shields/Insulation: Minimize uneven heating.
Support Redesign: Add guides/anchors to reduce cantilever loads.
Upgrade Materials: Switch to ASTM A182 F316L for cyclic thermal services.
4. Repair Solutions
A. Machining
On-Site Lathe Machining: Restore flatness (<0.03mm tolerance).
Metal Spray Coating: Rebuild eroded sealing surfaces.
B. Reinforcement
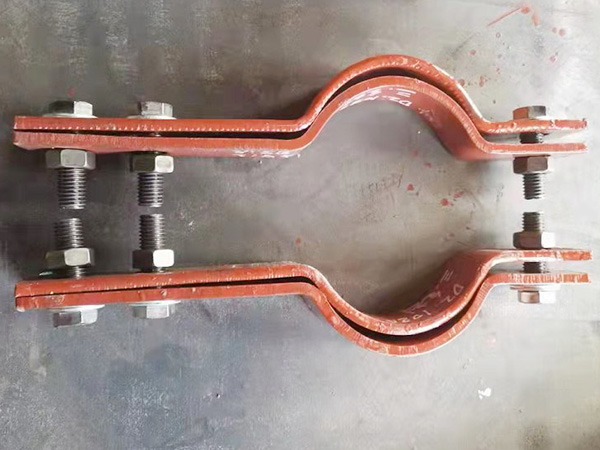
Stiffener Rings: Welded to distorted flanges for added rigidity.
Split Repair Clamps: Temporary leak sealing without downtime.
C. Replacement
High-Tolerance Flanges: ASME B16.47 Series A/B for large diameters.
Flexible Couplings: Replace rigid flanges in vibration-prone areas.
5. Industry-Specific Fixes
Power Plants: Use lap-joint flanges for thermal expansion loops.
Offshore Platforms: Corrosion-resistant overlays (Inconel 625) on carbon steel flanges.
Cryogenic Systems: Austenitic stainless steels to resist brittle fracture.
Proactive Measures:
✔ Flange Flatness Checks during maintenance shutdowns.
✔ Bolt Load Audits every 5,000 operational hours.
✔ Operator Training on proper assembly techniques.
Need a custom solution? Provide:
Flange material/size
Operating temp/pressure
Distortion photos or scan data
 Hot Products
Hot Products
 Contact Us
Contact Us
Contact:
Mobile:+86 +86 19133378808
Website:mingdepipe.com
Address: