Pipe Clamp Factory Production Workflow Explained
Author:Mingde Time:2026-02-13 16:44:29 Click:150
In industrial piping, construction, and infrastructure systems, pipe clamps play a crucial role in securing, supporting, and positioning pipelines. Behind every reliable clamp is a professional Pipe Clamp Factory that combines engineering knowledge with structured production workflows and scalable manufacturing capacity.
For any modern pipe clamp manufacturer, efficiency, quality, and consistency begin inside the factory. From raw material preparation to bulk shipment, each step in production influences clamp strength, dimensional accuracy, and long-term service life. This article explains how a pipe clamp factory organizes its production workflow and why these processes matter for large-scale industrial supply.
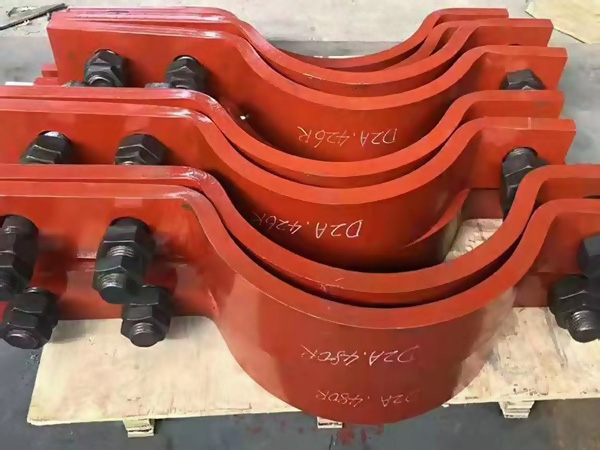

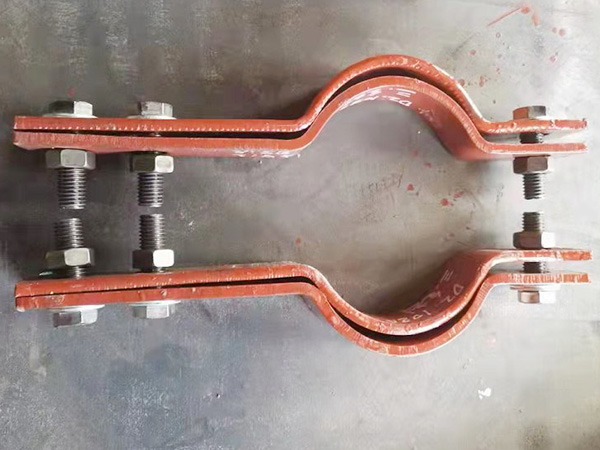
The Role of a Pipe Clamp Factory in Industrial Projects
A pipe clamp factory does more than simply assemble components. It acts as a complete manufacturing system responsible for:
·Material selection
·Forming and machining
·Surface protection
·Quality inspection
·Packaging and logistics
As infrastructure projects grow in size and complexity, buyers rely on manufacturers that can support stable factory production and dependable bulk supply. Understanding the workflow helps engineers and purchasers evaluate production capability and consistency.
Step 1: Raw Material Selection and Preparation
Every pipe clamp begins with raw materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, or alloy steel. Material quality directly impacts load capacity, corrosion resistance, and durability.
In a professional pipe clamp factory, production starts with:
·Chemical composition verification
·Mechanical property testing
·Surface defect inspection
·Batch traceability labeling
Prepared materials are cut, cleaned, and staged for forming. Manufacturer-level material control ensures that bulk manufacturing delivers uniform performance across large orders.
Step 2: Cutting and Forming Operations
After preparation, materials move into cutting and forming.
Common production methods include:
·Laser cutting for precise shapes
·Stamping for high-volume parts
·Bending and rolling for curved components
·Forging for heavy-duty clamps
Modern pipe clamp factories use automated machinery to maintain dimensional accuracy and speed. Consistent forming allows manufacturers to meet both small and large production requirements without sacrificing quality.
This stage defines the clamp’s structural geometry and load behavior, making it a critical part of factory manufacturing.
Step 3: Machining and Hole Processing
Once the basic shape is formed, machining refines the clamp.
Typical machining steps include:
·CNC drilling for bolt holes
·Slot milling for adjustment zones
·Thread tapping
·Edge chamfering
Precision machining ensures that pipe clamps assemble correctly and distribute loads evenly. Factory production systems rely on CNC automation to control tolerances across thousands of units, supporting stable bulk supply for industrial projects.
Step 4: Welding and Assembly
Some pipe clamp designs require welded joints or integrated components.
In this production stage, manufacturers apply:
·Robotic or manual welding
·Fixture-based alignment
·Heat control for distortion prevention
·Structural inspection
Assembly may also include rubber linings, vibration pads, or secondary fasteners. Controlled factory production ensures every assembled clamp meets design requirements before moving forward.
A professional pipe clamp factory balances speed and precision to support high-volume manufacturing without compromising joint integrity.
Step 5: Surface Treatment and Protection
Pipe clamps often operate in corrosive or outdoor environments. Surface treatment protects the metal and extends service life.
Common production finishes include:
·Hot-dip galvanizing
·Electroplating
·Powder coating
·Painting
·Passivation for stainless steel
Factory production lines integrate cleaning, coating, curing, and inspection in sequence. Manufacturers monitor coating thickness and adhesion to ensure long-term corrosion resistance in bulk manufacturing.
This step is essential for pipe clamp reliability in construction, HVAC, water, and industrial applications.
Step 6: Quality Control and Testing
Quality assurance is embedded throughout pipe clamp production, but final inspection ensures performance consistency.
Pipe clamp factory testing includes:
·Dimensional measurement
·Load testing
·Surface defect inspection
·Coating thickness checks
·Assembly verification
Batch records track each production lot, supporting traceability and accountability. Manufacturer-grade quality control builds confidence for buyers ordering large quantities for infrastructure and industrial projects.
Step 7: Packaging and Bulk Supply Preparation
After approval, pipe clamps are prepared for delivery.
Packaging focuses on:
·Damage prevention
·Moisture protection
·Easy handling
·Inventory identification
Bulk supply preparation may include palletizing, container loading plans, and logistics coordination. A professional pipe clamp factory designs packaging that protects products while improving transport efficiency for global projects.
Reliable factory production combined with smart logistics ensures on-time delivery for large-volume orders.
Automation and Digital Control in Pipe Clamp Production
Modern pipe clamp factories increasingly integrate automation and digital systems into production workflows.
Benefits include:
·Real-time production monitoring
·Reduced human error
·Faster cycle times
·Data-driven quality control
·Improved batch consistency
By applying digital manufacturing tools, pipe clamp manufacturers improve scalability while maintaining performance standards across mass production.
Production Flexibility for Custom and Standard Clamps
Not all projects use the same clamp design. A capable pipe clamp factory supports both:
·Standard catalog clamps
·Custom-engineered solutions
Flexible production lines allow manufacturers to switch tooling, adjust dimensions, and change materials without interrupting factory manufacturing schedules. This flexibility is essential for serving construction, energy, and industrial sectors simultaneously.
Why Production Workflow Matters to Buyers
Understanding factory workflow helps buyers evaluate supplier reliability.
A structured pipe clamp factory workflow delivers:
·Consistent quality
·Predictable lead times
·Scalable bulk supply
·Reduced defect risk
·Long-term performance
For engineers and procurement teams, choosing a manufacturer with strong production systems reduces project risk and operational cost.
Conclusion: Inside the Value of a Pipe Clamp Factory
In conclusion, the performance of every pipe clamp begins inside a professional Pipe Clamp Factory. From raw material inspection and forming to machining, surface treatment, and bulk shipment, each production stage influences reliability and service life.
By integrating advanced factory production systems and scalable manufacturing processes, a pipe clamp manufacturer ensures consistent quality and dependable bulk supply for industrial and construction projects.
For infrastructure, HVAC, and pipeline applications, working with a pipe clamp factory that controls its production workflow is the foundation for secure, efficient, and long-lasting pipeline support solutions.
References
GB/T 7714:Link R E. An introduction to the design and behavior of bolted joints[J]. Journal of Testing and Evaluation, 1991, 19(5): 417-418.
MLA:Link, R. E. "An introduction to the design and behavior of bolted joints." Journal of Testing and Evaluation 19.5 (1991): 417-418.
APA:Link, R. E. (1991). An introduction to the design and behavior of bolted joints. Journal of Testing and Evaluation, 19(5), 417-418.
 Hot Products
Hot Products
 Contact Us
Contact Us
Contact:
Mobile:+86 +86 19133378808
Website:mingdepipe.com
Address: