Testing Methods for Pipeline Insulation Brackets in Extreme Conditions
Author:Mingde Time:2025-12-07 13:59:55 Click:87
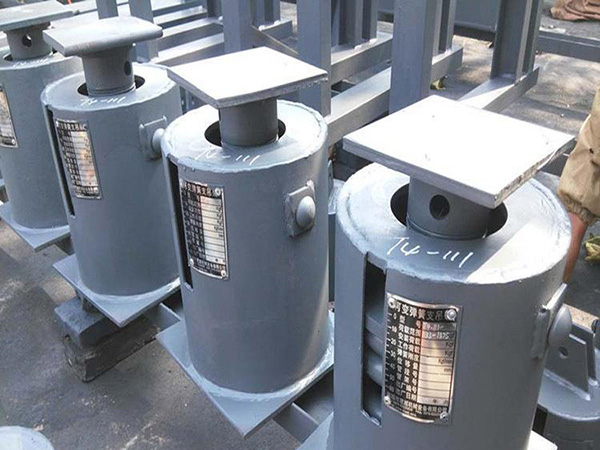
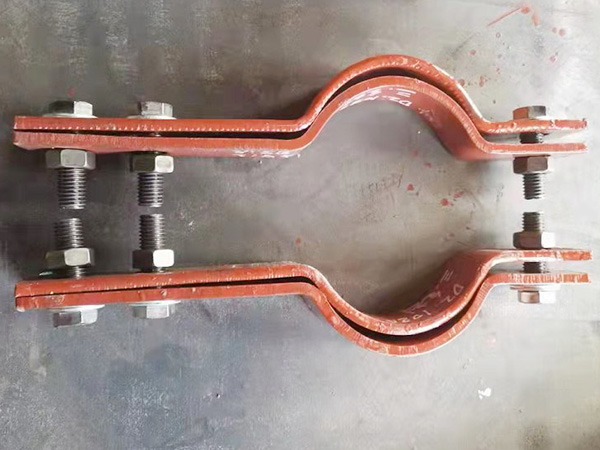
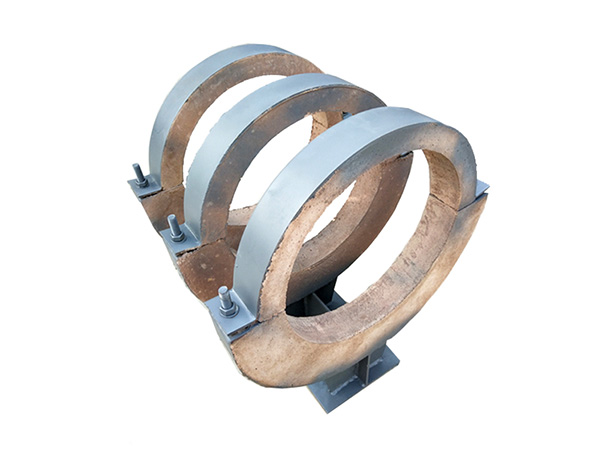
In industrial energy systems, the Pipeline Insulation Bracket is a critical support component that stabilizes insulated pipelines, minimizes thermal transfer, and maintains the structural integrity of a system under demanding conditions. When these brackets are produced by a genuine manufacturer with proven production capacity and the ability to maintain consistent bulk supply, end users gain confidence that the components have undergone proper engineering validation.
However, pipelines rarely operate in mild conditions. Whether in petrochemical facilities, cryogenic plants, transportation terminals, or high-temperature districts, brackets must endure extreme stresses that could easily compromise their performance. To ensure reliability, engineers subject Pipeline Insulation Brackets to a series of specialized tests designed to simulate real-world extremes. The following sections outline the most essential testing methods used today.


1. Thermal Shock and Temperature Cycling Evaluations
One of the toughest challenges a Pipeline Insulation Bracket faces is exposure to sudden or repeated temperature swings. These can range from cryogenic lows to extreme surface heat depending on the pipeline’s function.
How temperature testing is conducted
Brackets are placed in controlled chambers and exposed to alternating cycles of:
·Severe cold, sometimes reaching –196°C
·High heat, often exceeding several hundred degrees Celsius
This repetitive temperature change replicates the operational fluctuations pipelines endure during process variations or starting and stopping cycles.
What engineers look for
·Thermal expansion and contraction resistance
·Cracking, delamination, or insulation breakdown
·Material fatigue after extended cycling
·Deformation affecting load-bearing ability
Only brackets engineered with advanced materials and reinforced insulation structures can consistently withstand such extreme shifts.
2. Load, Compression, and Structural Strength Testing
Every Pipeline Insulation Bracket must support both the weight of the pipe and the weight of the media flowing inside it. Because this load is substantial, mechanical strength testing is essential.
Testing includes
·Static load application to simulate operational weight
·Dynamic loading representing pressure fluctuations or surge conditions
·Impact loads to mimic accidental stress events
Key evaluation points
·Permanent deformation after heavy loading
·Buckling resistance
·Compression capability of the insulation core
·Stability under long-duration stress
Manufacturers with organized production processes typically incorporate this testing as part of their quality-control protocol to certify each bracket’s load capacity.
3. Vibration and Cyclic Fatigue Tests
Vibration is inevitable in systems that rely on pumps, fans, compressors, and rotating machinery. Over time, minor vibrations can evolve into destructive forces if the brackets are not engineered to handle them.
Why vibration testing is critical
This testing:
·Reveals weaknesses in fasteners, joints, and mounting surfaces
·Helps evaluate insulation degradation under oscillating forces
·Determines how long a bracket can operate under repetitive stress cycles
Advanced vibration tables simulate high-frequency stresses over thousands of operational hours to predict fatigue-related failures long before they appear in the field.
4. Corrosive Environment and Weathering Tests
Depending on the installation site, brackets may be exposed to corrosive chemicals, seawater, humidity, or environmental pollutants. Corrosion testing replicates such exposures.
Typical tests include
·Salt fog / salt spray simulations
·Chemical immersion in corrosive liquids or vapors
·UV aging for outdoor installations
·High-humidity environmental chamber analysis
What the results show
·Corrosion resistance of metals and coatings
·Stability of insulation materials over time
·Oxidation rate and protective layer durability
·Structural integrity after prolonged environmental exposure
Brackets that perform well in these conditions often use stainless steel alloys or composite materials built for long-term corrosion mitigation.
5. Fire Exposure and High-Temperature Endurance Tests
Pipelines carrying flammable or high-energy materials require brackets capable of performing under fire conditions. Fire-resistance testing simulates these emergencies.
Fire testing typically examines
·Structural retention at elevated temperatures
·Insulation effectiveness during flame exposure
·Hardware integrity under fire load
·Resistance to thermal breakdown and flame spread
This testing ensures that the Pipeline Insulation Bracket continues to function long enough for emergency protocols to take effect.
6. Cryogenic Impact Testing
Cryogenic pipelines—carrying LNG, nitrogen, hydrogen, or similar media—place brackets under some of the harshest conditions possible.
Cryogenic testing evaluates
·Material brittleness at extremely low temperatures
·Insulation cracking or fragmentation
·Load performance in cryogenic environments
·Layer separation or delamination under rapid cooling
Because low temperatures dramatically reduce material ductility, only brackets engineered with cryogenic-rated materials can pass this evaluation.
7. Digital Simulation Through FEA and Computational Modeling
Modern engineering relies heavily on computational tools to predict failure points before physical prototypes are ever built.
FEA simulations include
·Mechanical stress mapping
·Thermal distribution calculations
·Vibration resonance identification
·Predictive failure modeling
Although computational testing cannot replace physical validation, it helps refine bracket geometry and material selection, reducing waste and improving overall production efficiency.
Conclusion: Rigorous Testing Ensures Safe and Reliable Pipeline Operation
A Pipeline Insulation Bracket is far more than a structural accessory—it is a core component that influences safety, efficiency, and system lifespan. When these brackets are sourced from an experienced manufacturer with proven production consistency and dependable bulk supply, users benefit from components backed by detailed engineering evaluation.
Through temperature cycling, mechanical loading, vibration analysis, corrosion testing, fire exposure, and cryogenic evaluation, each test strengthens the reliability profile of the bracket. As industrial environments become more complex and performance demands rise, thorough testing remains the foundation for ensuring pipeline systems operate safely and efficiently.
References
GB/T 7714:Baetens R, Jelle B P, Gustavsen A. Aerogel insulation for building applications: A state-of-the-art review[J]. Energy and buildings, 2011, 43(4): 761-769.
MLA:Baetens, Ruben, Bjørn Petter Jelle, and Arild Gustavsen. "Aerogel insulation for building applications: A state-of-the-art review." Energy and buildings 43.4 (2011): 761-769.
APA:Baetens, R., Jelle, B. P., & Gustavsen, A. (2011). Aerogel insulation for building applications: A state-of-the-art review. Energy and buildings, 43(4), 761-769.
 Hot Products
Hot Products
 Contact Us
Contact Us
Contact:
Mobile:+86 +86 19133378808
Website:mingdepipe.com
Address: