Standard Procedure for Pipe Support and Hanger Installation
Author:Mingde Time:2025-04-29 01:06:42 Click:158
The installation of pipe supports and hangers plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity, functionality, and longevity of piping systems across industrial facilities. A standardized process ensures proper load distribution, accommodates thermal movement, and prevents mechanical failure due to misalignment or stress.
This article outlines the standard procedure for the installation of pipe supports and hangers, from preparation to final inspection.
1. Pre-Installation Preparation
a. Review of Design Drawings
Verify the layout of support points based on isometric drawings, pipe routing diagrams, and structural plans.
Confirm the type, size, load rating, and location of each support/hanger.
b. Material and Tool Inspection
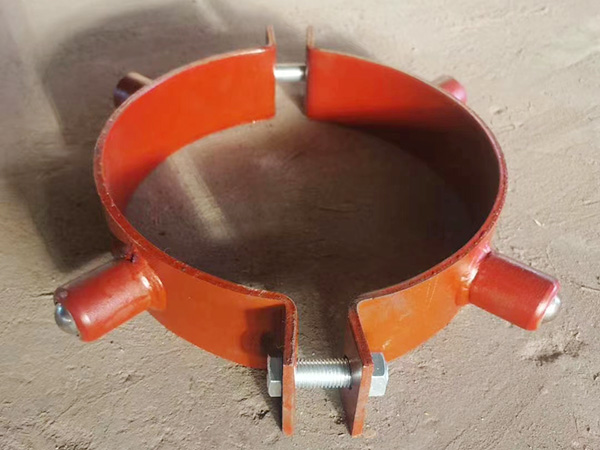
Check all support components (clamps, rods, brackets, springs, anchors) for damage, corrosion, or missing parts.
Ensure tools (torque wrenches, levels, laser alignment tools) are available and calibrated.
c. Site Condition Assessment
Confirm structural members or anchoring points are ready and accessible.
Clear any obstructions in the installation area.
2. Marking and Positioning
Mark the precise location of each support or hanger according to the approved layout.
Use measuring tapes, levels, and laser tools to ensure vertical/horizontal alignment.
Ensure adequate clearance for pipe expansion, insulation, and maintenance access.
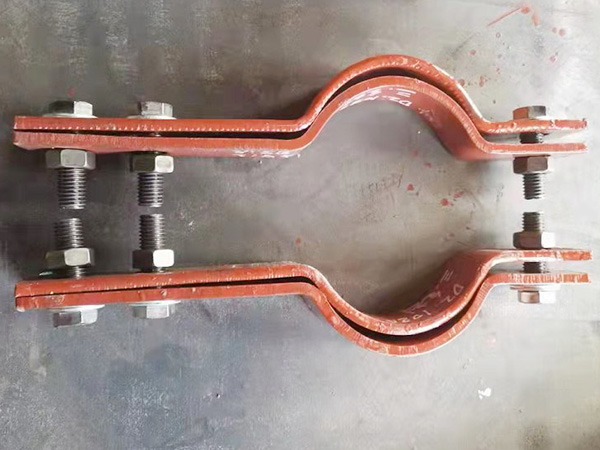
3. Installation of Structural Attachments
Secure anchor bolts, brackets, or baseplates to structural elements such as beams, ceilings, or walls.
For overhead installations, ensure welding or bolting follows load-bearing and safety standards.
Torque bolts or welds according to design specifications.
4. Assembly of Support Components
a. For Rigid Supports
Install clamps, shoes, or trunnions directly onto the pipe or beneath it.
Align support centerlines with pipe axis.
b. For Hangers
Attach hanger rods, springs, or sway braces to their respective anchors.
Adjust length to maintain proper elevation of the pipe.
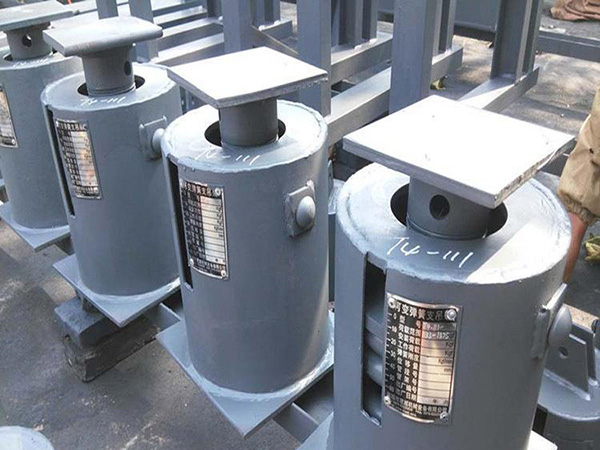
c. For Spring Supports
Pre-set variable or constant spring hangers according to cold/hot load settings.
Install travel indicators to monitor movement during operation.
5. Pipe Alignment and Load Transfer
Place the pipe onto supports, ensuring it rests evenly on sliding or rigid surfaces.
Adjust vertical supports to achieve the designed pipe slope or elevation.
Transfer load gradually onto spring supports if present. Avoid sudden loading.
6. Expansion, Movement, and Clearance Check
Confirm sliding or guided supports are free to move in the direction of thermal expansion.
Ensure insulation space is maintained around the pipe.
Verify that guides and anchors are correctly oriented.
7. Final Tightening and Adjustment
Recheck all fasteners, anchor bolts, and rod lengths.
Torque to specified values using calibrated tools.
For spring supports, ensure the cold setting matches the design.
8. Quality Inspection and Documentation
Conduct a thorough inspection to check:
Correct placement and orientation of supports
Free movement at expansion points
No excessive gaps, misalignment, or visible stress
Document support installation with photos, torque records, and inspection reports.
Sign off by quality control and engineering teams.
Conclusion
Following a standardized pipe support and hanger installation procedure ensures the safe and efficient functioning of the entire piping system. Proper installation prevents premature wear, misalignment, and potential damage due to thermal or dynamic loads. With accurate planning, careful execution, and strict adherence to specifications, installation teams can ensure reliable and long-term performance of both the pipe system and its supporting infrastructure.
 Hot Products
Hot Products
 Contact Us
Contact Us
Contact:
Mobile:+86 +86 19133378808
Website:mingdepipe.com
Address: