Selection Strategy for Pipe Supports and Hangers in Industrial Piping Systems
Author:Mingde Time:2025-04-29 01:07:59 Click:93
Pipe supports and hangers are essential mechanical components that ensure the structural integrity, stability, and functionality of industrial piping systems. A correct selection strategy is crucial to accommodate thermal expansion, dynamic loads, vibration, and system alignment.
This article outlines a comprehensive selection strategy for pipe supports and hangers based on design conditions, functional requirements, and operating environments.
1. Understand the Purpose of Support Systems
Before selecting any support or hanger type, it’s essential to define the role it will play:
Load Bearing: Support the weight of the pipe, fluid, insulation, and fittings.
Thermal Expansion Accommodation: Allow movement caused by temperature variations.
Vibration Control: Dampen oscillations from pumps, compressors, or flow turbulence.
Alignment Maintenance: Keep the pipe in its designed position.
Seismic or Wind Load Resistance: Withstand external environmental forces.
2. Analyze System Parameters
a. Pipe Size and Weight
Larger diameter and thicker-walled pipes require more robust supports.
Consider total load including fluid, insulation, and fittings.
b. Temperature and Expansion
Determine thermal expansion ranges to decide between fixed, sliding, or spring supports.
For high-temperature pipelines, constant or variable spring hangers may be required.
c. Pressure and Flow
High-pressure systems may require supports with minimal movement tolerance.
Pulsating flow may necessitate vibration-damping designs.
d. Location and Orientation
Horizontal pipelines often require a mix of rigid and guided supports.
Vertical runs may need guide clamps and anchors to prevent swaying or sliding.
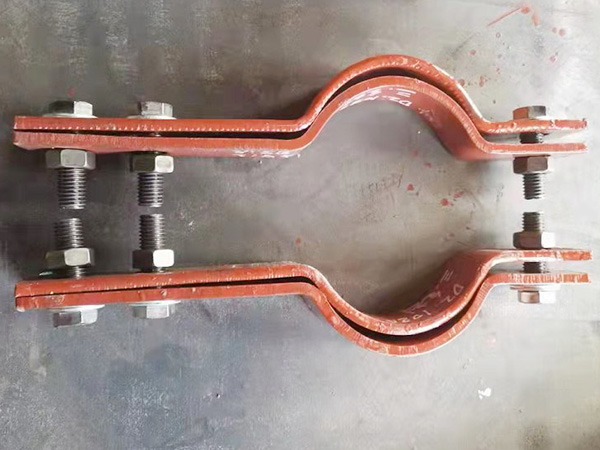
3. Choose the Appropriate Support Type
Based on the function and environment, select from the following:
Rigid Supports
For static conditions with little thermal movement.
Ideal for underground or floor-mounted installations.
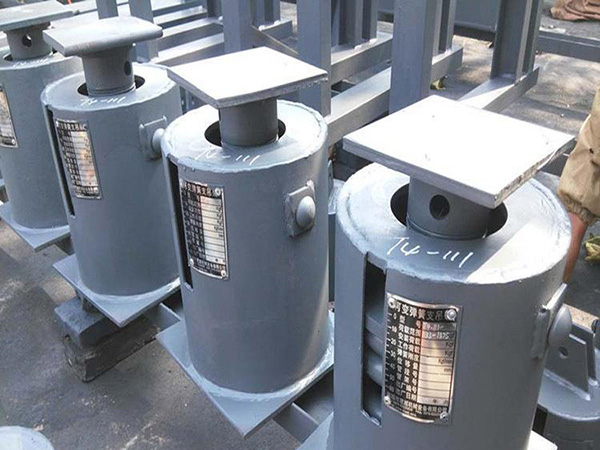
Spring Supports (Variable/Constant)
Used when thermal vertical movement must be supported without excessive stress.
Required in steam systems, high-temperature chemical lines, or near boilers.
Sliding Supports
Allow horizontal movement while supporting vertical loads.
Often used in long pipe runs or overhead rack systems.
Guide Supports
Control lateral displacement while permitting axial movement.
Positioned near expansion joints or bends.
Anchors and Fixed Points
Restrict all movement; strategically placed to isolate expansion zones.
Crucial for force direction control and pipe stress analysis.
Vibration Isolators
Includes snubbers or dampers to reduce vibration and noise.
Essential in high-speed machinery areas.
4. Consider Environmental Conditions
Corrosive Environments: Use stainless steel or coated supports.
Outdoor Exposure: Ensure weatherproof materials and UV protection.
Seismic Zones: Select supports compliant with seismic codes (e.g., ASCE, GB50909).
Clean Rooms or Food Plants: Require hygienic designs and minimal contamination risk.
5. Compliance with Standards
Ensure the selected supports comply with international or national standards, such as:
ASME B31.1/B31.3 (for power and process piping)
MSS-SP-58 and MSS-SP-69 (for pipe hangers and supports)
GB/T 17116 (China pipe support standards)
ISO 14692 (for composite piping systems)
6. Optimization by Location
a. Near Equipment
Use flexible or vibration-dampening supports to reduce stress transfer to equipment.
b. Near Bends or Branches
Use guides or supports to stabilize directional forces.
c. Long Straight Runs
Combine sliding and anchor supports to accommodate expansion while controlling pipe motion.
7. Use of Support Selection Software
Modern piping design often incorporates software (e.g., CAESAR II, AutoPIPE) for support layout and stress analysis. These tools help:
Identify optimal support locations
Calculate reaction loads and thermal effects
Reduce manual errors in selection
Conclusion
An effective pipe support and hanger selection strategy ensures mechanical safety, thermal performance, and system longevity. By integrating pipe characteristics, environmental factors, and dynamic forces, engineers can choose the most suitable support solutions tailored to the specific needs of industrial piping systems.
 Hot Products
Hot Products
 Contact Us
Contact Us
Contact:
Mobile:+86 +86 19133378808
Website:mingdepipe.com
Address: