Key Points for the Daily Maintenance of Pipe Supports and Hangers
Author:Mingde Time:2025-04-29 01:09:44 Click:199
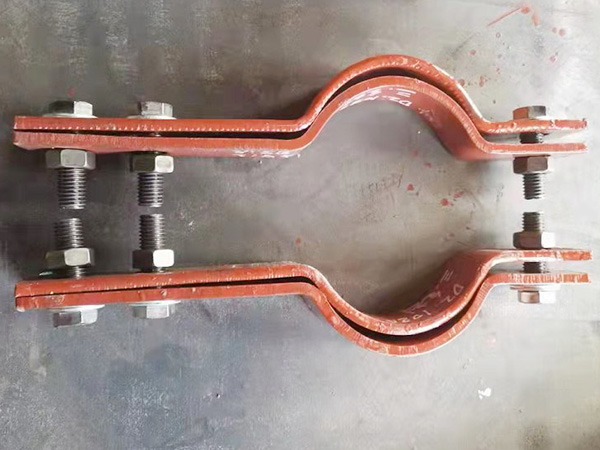
Pipe supports and hangers are essential components that maintain the alignment, stability, and structural integrity of piping systems. Over time, environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and operational conditions may cause wear, misalignment, or failure. Therefore, regular maintenance is critical to ensure optimal performance and to prevent system malfunctions.
Below are the core elements and best practices for the daily maintenance of pipe supports and hangers.
1. Visual Inspection
a. Check for Corrosion or Rust
Inspect metallic components such as clamps, rods, brackets, and base plates for surface corrosion.
In coastal or chemical plant environments, prioritize areas with high humidity or chemical exposure.
Apply anti-corrosive coatings or replace severely corroded parts.
b. Observe for Physical Deformation
Look for bent rods, shifted supports, cracked welds, or displaced anchors.
Misalignment may indicate overloading, thermal expansion issues, or structural movement.
c. Examine Insulation Clearance
Ensure the support allows adequate space for insulation materials.
If insulation is compressed or damaged at support points, adjust or replace components.
2. Mechanical Tightness Check
a. Fasteners and Anchors
Confirm that all bolts, nuts, and anchor points are tight and free of loosening due to vibration or thermal cycling.
Retorque according to specified torque values if needed.
b. Spring Supports
Check that spring supports have not seized or deviated from the preset position.
Read and record travel indicators to detect unusual load shifts.
c. Hanger Rods and Guides
Ensure rods remain plumb and guides are aligned.
Misalignment can lead to uneven load distribution and stress concentration.
3. Movement and Load Monitoring
a. Thermal Movement
Observe that sliding supports or rollers move freely and are not obstructed by debris or rust.
If supports appear stuck, clean the surfaces and lubricate moving parts as appropriate.
b. Load Transfer
Ensure that spring and constant hangers are sharing loads as designed.
If load is unevenly transferred, it may affect the performance of adjacent piping or equipment.
4. Cleaning and Lubrication
Remove dust, dirt, oil, and moisture from exposed support surfaces.
Lubricate sliding pads, roller supports, and rotating joints to maintain smooth operation.
Avoid excessive lubricant use, which can attract dirt and accelerate wear.
5. Replacement of Worn Components
Replace damaged or aged components such as rubber pads, U-bolts, springs, or isolators.
If cracks or metal fatigue are observed, discontinue use and install new parts immediately.
Always use parts that match original specifications and load ratings.
6. Record Keeping and Scheduling
Maintain a log of all inspections, findings, adjustments, and replacements.
Assign regular maintenance intervals based on pipe system criticality (e.g., monthly for high-temp lines, quarterly for standard water systems).
Use digital asset management systems or maintenance software where possible.
7. Special Attention Areas
Focus on supports near pumps, valves, and rotating equipment due to higher vibration.
Inspect supports in high-temperature or cryogenic zones more frequently.
Check rooftop or outdoor supports after extreme weather events such as storms or snow.
Conclusion
Proper and timely maintenance of pipe supports and hangers not only extends their service life but also enhances the overall safety and efficiency of the piping system. Through a disciplined approach involving inspection, tightening, lubrication, and record management, maintenance teams can ensure stable operation, reduce downtime, and prevent costly failures.
 Hot Products
Hot Products
 Contact Us
Contact Us
Contact:
Mobile:+86 +86 19133378808
Website:mingdepipe.com
Address: